Japanese Encephalitis
Vaccination
Protect yourself against Japanese Encephalitis, a serious viral infection transmitted by mosquitoes. Get vaccinated at Cleckheaton Pharmacy or book online today!
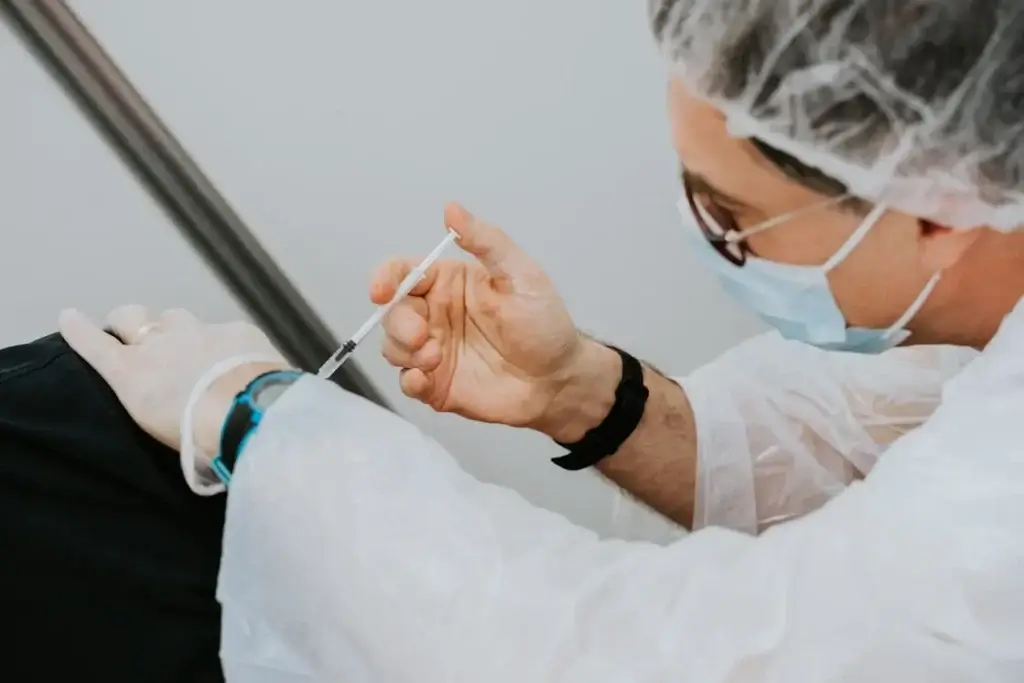


What is Japanese Encephalitis?
Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is a serious viral brain infection spread by infected mosquitoes. It can lead to severe complications such as brain inflammation, seizures, paralysis, and even death. The virus is most common in rural areas of Asia and the Western Pacific, particularly where rice paddies and pig farms provide an ideal breeding ground for mosquitoes.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection and protect your long-term health.
Symptoms of Japanese Encephalitis

High Fever

Headache

Confusion

Seizures
Muscle weakness
Japanese Encephalitis Prevention & Transmission
Prevention of Japanese Encephalitis
- Vaccination before travelling to high-risk areas.
- Using insect repellent and wearing long-sleeved clothing.
- Avoiding mosquito-infested areas, especially during peak activity times.
Transmission of Japanese Encephalitis
Japanese Encephalitis is not spread from person to person. Instead, it is transmitted through the bite of an infected Culex mosquito.
🔹 Bites from infected mosquitoes (mainly in rural, agricultural regions)
🔹 Virus circulates between mosquitoes, pigs, and birds
🔹 Humans are infected accidentally but do not spread the virus further
The risk of infection is higher during the rainy season and in areas with stagnant water.
High-risk Areas for Japanese Encephalitis
Asia
- India
- China
- Japan
- South Korea
- Indonesia
Southeast Asia
- Thailand
- Malaysia
- Vietnam
Ready to Protect your Health?
Why Choose Us
At Cleckheaton Pharmacy, your health comes first! Our expert team is dedicated to providing advice and treatment tailored to your needs.
Effortless Service
Say goodbye to stress! Book your appointment online or visit at a time that works for you. We're here to accommodate your busy schedule.
The Outcome
Feel secure and enjoy the peace of mind that comes with safeguarding your health—make proactive choices leading to a lifetime of well-being.
Commonly Asked Questions
Do I really need the Japanese encephalitis vaccine?
The Japanese encephalitis vaccine is recommended for individuals travelling to regions where the virus is prevalent, particularly if:
- You’re staying for more than a month.
- You’re visiting rural areas, such as rice fields or pig farming regions.
- You plan to engage in extensive outdoor activities.
For shorter trips, the vaccine may be considered if your activities or destinations put you at increased risk. It’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to assess your specific risk factors.
Who is eligible for the Japanese encephalitis vaccine?
The vaccine is suitable for individuals aged 6 months and older who are at risk of exposure to the virus due to their travel plans or occupational hazards. Eligibility is primarily determined by the likelihood of encountering the virus in endemic areas.
What are the odds of getting Japanese encephalitis?
Japanese encephalitis is rare among travellers; most infections occur in rural parts of Asia. The overall risk is low, but it increases for those spending extended periods in endemic regions, especially during the transmission season and in areas with high mosquito activity.
Is the Japanese encephalitis vaccine free on NHS?
No, the Japanese encephalitis vaccine is not available for free on the NHS. Travellers usually need to obtain it privately from travel clinics or pharmacies such as The Cleckheaton Pharmacy.
How long does a Japanese encephalitis jab last?
The standard vaccination course consists of two doses administered at least 7 days before your departure. Full immunity is achieved approximately one week after the second dose. A booster dose is recommended if you continue to be at risk, typically between 12 to 24 months after the initial vaccination.
What are the side effects of the Japanese encephalitis vaccine?
The Japanese encephalitis vaccine is generally well-tolerated, but like all vaccines, it can cause side effects. Most reactions are mild and temporary. Common side effects include:
- Injection site reactions: Pain, redness, swelling, or soreness at the site of vaccination.
- Systemic reactions: Fever, headache, muscle aches, fatigue, and nausea.
These symptoms typically resolve within a few days. In rare cases, individuals may experience allergic reactions, such as skin rash, itching, hives, or swelling of the face, lips, or tongue. Severe allergic reactions are extremely uncommon.
If you experience any severe or persistent side effects after vaccination, it’s important to seek medical advice promptly.

